Understanding What Is the Forex (FX) Market
The forex market is an international, decentralised market where currencies are bought and sold 24 hours a day, five days a week. It is not concentrated in a location. Instead, it is traded electronically OTC on the grounds of an electronic network of banks, brokers, financial institutions, and individuals.
Foreign exchange is also known as Forex or FX. The Forex market is the world’s largest and most liquid financial market. It exchanges currencies as part of its function in the global economy. Whether we are travellers visiting other nations or multinational companies making foreign transactions, we interact with the Forex market directly or indirectly.
Due to its liquidity and wide range of currency pairs, traders seek Forex. Traders can earn money by monitoring and analyzing the currency pairs they are familiar with.

Key Characteristics:
- Open 24 hours/day, 5 days/week
- $7.5 trillion (approx.) in daily trading volume
- Highly liquid and accessible to both institutional and retail traders
- Operates across major financial centres: London, New York, Tokyo, Sydney
How Does Forex Trading Work?
Trading takes place in currency pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro against the US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound against the Japanese Yen). In these pairs, the first currency listed is the base currency, while the second is the quote currency. Traders aim to profit by taking advantage of differences in exchange rates, typically by buying low and selling high, or vice versa.
Example:
If you believe the Euro will strengthen against the US Dollar, you can buy EUR/USD. If the exchange rate increases, you can sell for a profit.
Types of Forex Pairs
- Major Pairs – Most widely traded and include USD (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/USD)
- Minor Pairs – Don’t include USD but do include major currencies (e.g., EUR/GBP)
- Exotic Pairs – Match a major currency against an emerging market currency (e.g., USD/TRY)
How Many Days of Forex Trading In A Year?
How many trading days are there in a year? Except for public holidays, the forex market is open every weekday, i.e., Monday through Friday. Therefore, except for significant holidays, foreign exchange trading days in a year will be between 250 and 252.
About 8 to 10 public holidays influence forex trading in large markets every year. So, the number of forex trading days after adjusting would be:
- 260 (total weekdays)
- Minus 8 to 10 holidays
- Equals approximately 250 to 252 trading days annually
Are All Forex Pairs Tradable During All Sessions?
In theory, most major currency pairs are 24/5 tradable since the forex market is decentralised and open 24 hours a day in major financial hubs worldwide from Monday to Friday.
Nevertheless, liquidity and volatility vary by sessions and pairs, and thus some pairs are more liquid and convenient to trade in some sessions:
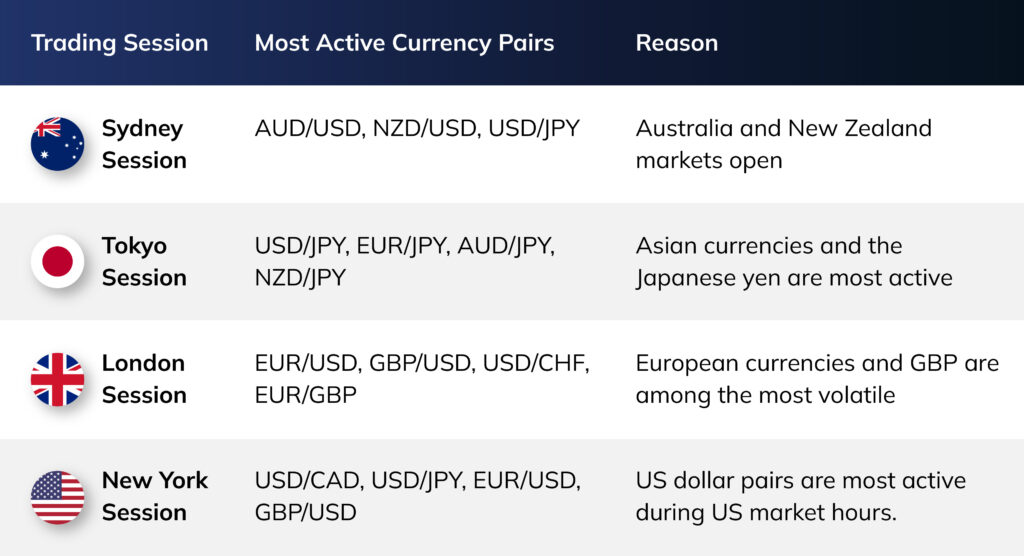
Summary:
- All pairs can technically be traded whenever the market is open.
- Liquidity and spreads are best when the relevant market is open, so trading a pair during its “home” session usually offers tighter spreads and better price action.
- During overlap sessions (e.g., London/New York), many pairs see increased volatility and volume, offering more trading opportunities.
Best Forex Pairs To Trade on Each Difference Session
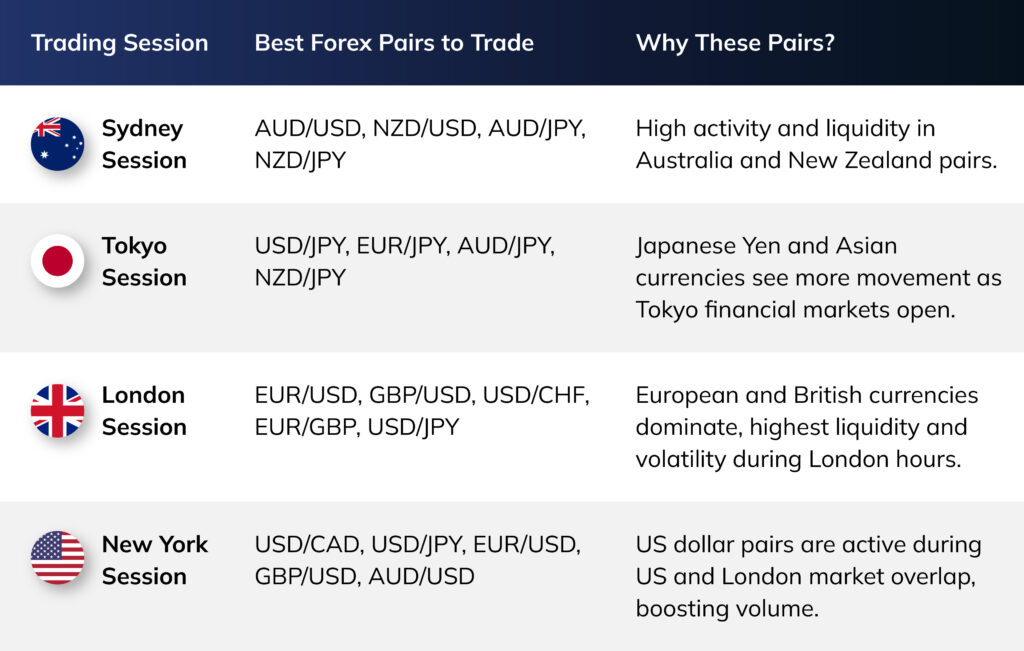
Additional Insights:
- The London/New York overlap, occurring between 1 PM and 5 PM GMT, is the most liquid and volatile period, offering ideal conditions for trading major currency pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY.
- It’s best to avoid trading exotic pairs during periods of low market activity, as spreads tend to widen and liquidity decreases.
- Aligning your trading pairs with your preferred session helps you take advantage of tighter spreads, stronger price movements, and reduced slippage risk.
Forex Trading Hours: Global Market Sessions
This continuous operation is divided into four main trading sessions based on the business hours of major financial hubs: Sydney, Tokyo, London, and New York. Due to market liquidity and volatility variations, each session offers unique trading opportunities.
| Trading Session | Market Open (Local Time) | Market Close (Local Time) | Market Open (GMT/UTC) | Market Close (GMT/UTC) |
| Sydney Session | 10:00 PM AEDT | 7:00 AM AEDT | 11:00 PM GMT | 8:00 AM GMT |
| Tokyo Session | 9:00 AM JST | 6:00 PM JST | 12:00 AM GMT | 9:00 AM GMT |
| London Session | 8:00 AM GMT | 5:00 PM GMT | 7:00 AM GMT | 4:00 PM GMT |
| New York Session | 8:00 AM EST | 5:00 PM EST | 12:00 PM GMT | 9:00 PM GMT |
- The Sydney session marks the start of the forex trading week and typically has lower liquidity compared to other sessions but is important for trading AUD and NZD pairs.
- The Tokyo session overlaps with Sydney and sees increased activity, especially in JPY and other Asian currencies.
- The London session is the largest market, generating the highest trading volume and volatility, particularly for EUR, GBP, and USD pairs.
- The New York session overlaps with London for a few hours daily, creating the most liquid and volatile trading periods, ideal for major currency pairs.
Important Notes:
- Forex trading hours shift with Daylight Saving Time (DST) changes in various countries.
- The market is closed on weekends (Saturday and Sunday) and certain public holidays.
- The London/New York overlap (1 PM to 5 PM GMT) is widely considered the most active and best time to trade.
Understanding these sessions helps traders optimize their strategies by focusing on periods with the best liquidity and price movement.
Who Participates in the Forex Market?
The forex market is diverse and includes:
- Central Banks: To control currency stability and implement monetary policy
- Commercial Banks: For global transaction settlement
- Corporations: To hedge against foreign currency exposure
- Hedge Funds and Institutional Investors: For speculation and portfolio diversification
- Retail Traders: Individuals using trading platforms for speculation or investment
Why Trade Forex?
- 24/5 Market: Trade anytime, 24/5, allowing flexibility.
- High Liquidity: $7.5 trillion daily trading volume, making entering or exiting trades easy.
- Leverage Opportunities: Trade large positions with relatively small capital (high risk)
- Diverse Strategies: Suitable for any scalping, day trading, swing trading, and long-term investing
- Global Accessibility: Trade from anywhere in the world with internet access
- Low Transaction Costs: Often low spreads and commissions.
- Transparency: Real-time pricing and market data for reference.
- Potential for Profit in Rising and Falling Markets: Short and Long Positions.
- Access to Global Markets: Trade currencies worldwide, gaining exposure to the momentum of international economies.
- Potential for High Returns: Opportunities for significant profit with proper analysis and strategy.
- Market News and Analysis: Access a wealth of information and tools to support your trading decisions.
Risks to Consider
While forex trading offers many opportunities, it also comes with risks, such as:
- High market volatility
- Use of leverage magnifies losses
- Lack of regulation in some jurisdictions
- Emotional and psychological challenges of trading
Good risk management, education, and strategy are the keys to long-term survival in the forex market.
Summary:
Last, the Forex (FX) market is a constituent part of the international financial system and offers unmatched trading opportunities for those well-versed in its structure and operation. Regardless of whether an experienced investor or a newcomer to investing with an interest in currency trading, it is imperative to gain a sound knowledge about Forex to be able to tackle this dynamic market with self-assurance.





